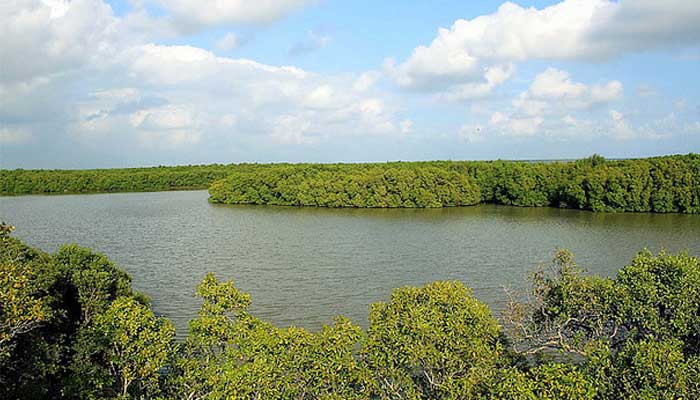
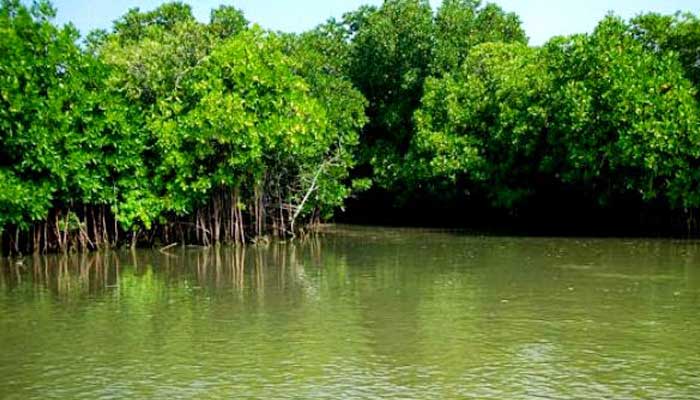
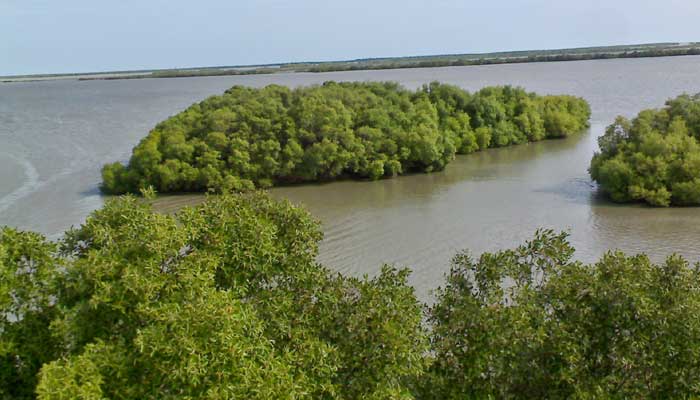
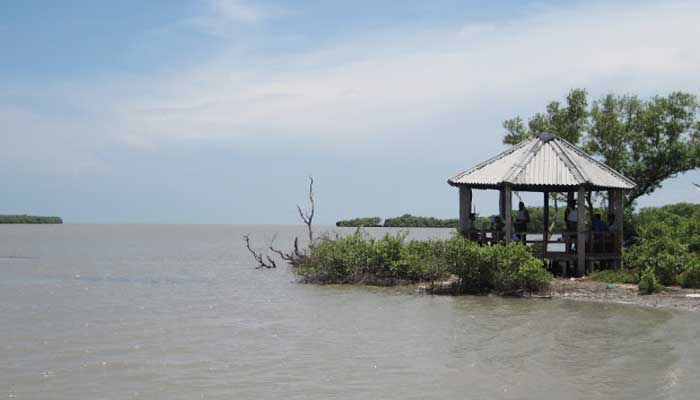
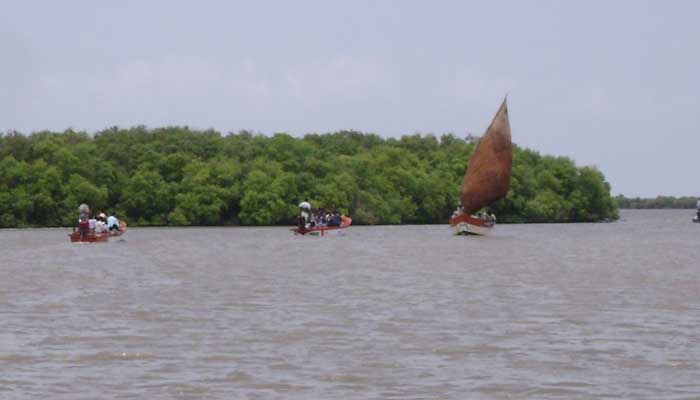
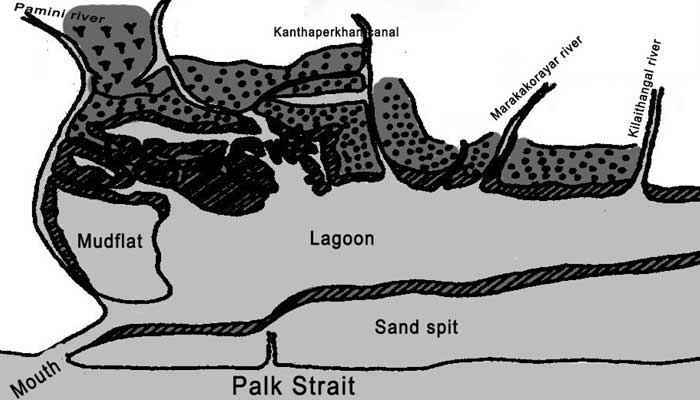
Muthupet a town in Tiruvarur District, located between Thiruthuraipoondi and Pattukkottai, is nearly around 360km away. The town lies adjacent to the Bay of Bengal and is in the southernmost part of the Cauvery delta. This town is bounded by two rivers Korayar and Pamaniyar, to the east and the west respectively. The rivers Koriayar and Pamaniyar join near Muthupet, and there is this lagoon.
This lagoon covers an area of approximately 6,803.01 ha of which only 4% is occupied by well-grown mangroves. The rivers Paminiyar, Koraiyar, Kilaithankiyar Marakkakoraiyar and other tributaries of the river Cauvery flow through Muthupet and adjacent villages. At the tail end, they form a lagoon before meeting the sea.